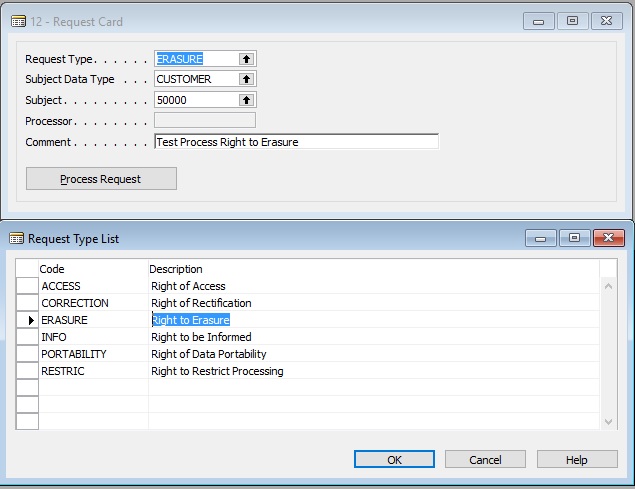
Right to Erasure
The right to erasure does not provide an absolute ‘right to be forgotten’. Individuals have a right to have personal data erased and to prevent processing in specific circumstances:
- Where the personal data is no longer necessary in relation to the purpose for which it was originally collected/processed
- When the individual withdraws consent
- When the individual objects to the processing and there is no overriding legitimate interest for continuing the processing
- The personal data was unlawfully processed (ie otherwise in breach of the GDPR)
- The personal data has to be erased in order to comply with a legal obligation
- The personal data is processed in relation to the offer of information society services to a child
- There are some specific circumstances where the right to erasure does not apply and you can refuse to deal with a request
The NAVGDPR toolset provides integrated functionality for the data controller to ‘erase’ a data subject’s personal data as catalogued in the application
To retain data referential integrity, records are not deleted, but the sensitive data items are replaced by asterisks
There may be other local legislation that overrides the GDPR in certain conditions (eg. An HMRC requirement to retain sales invoice details for 7 years) In this case, sensitive data items would then be encrypted instead
These rules are all configurable by data category within the setup of NAVGDPR